Table Of Content
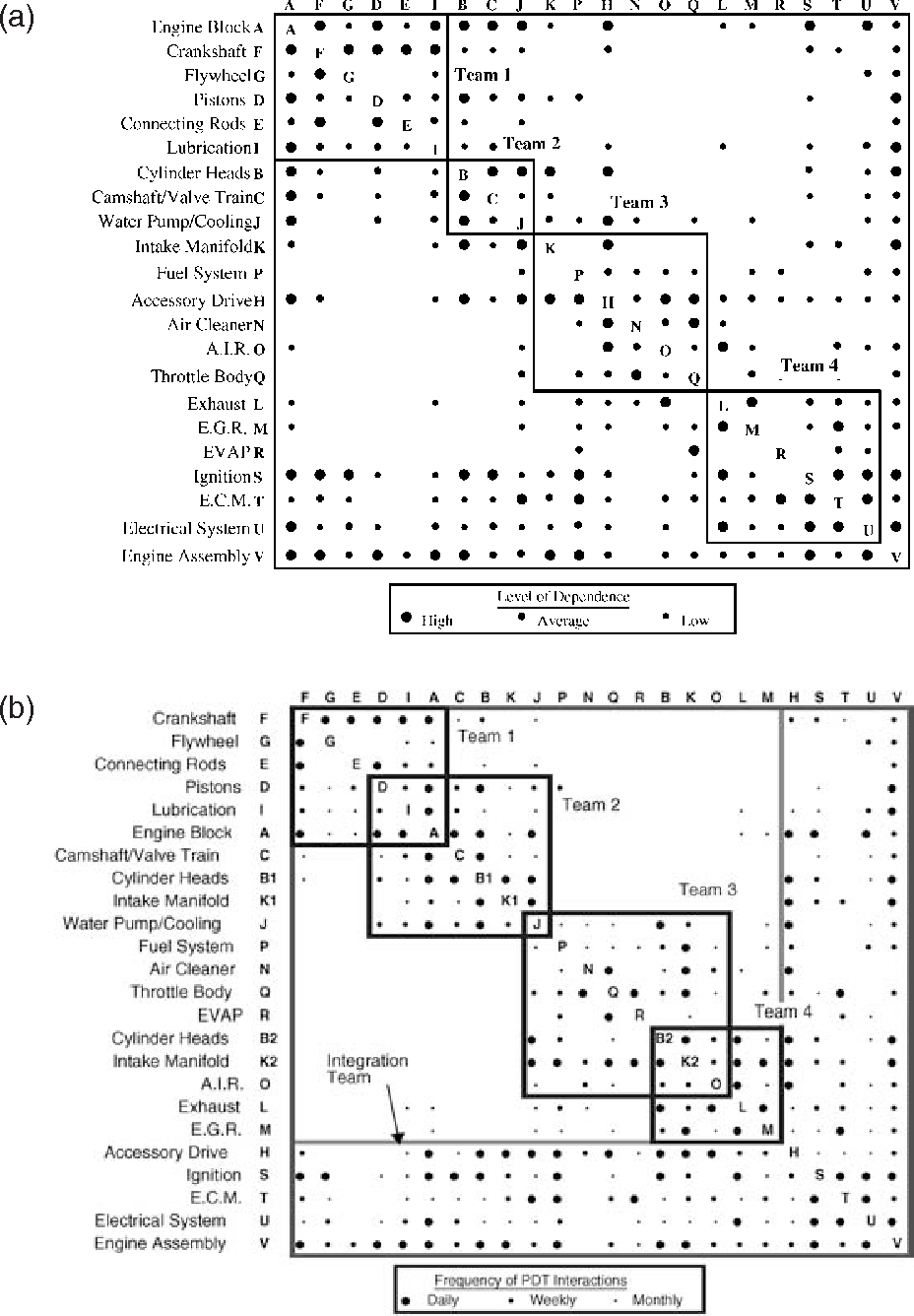
We next asked if there are other dependencies in Cascading Choices, that the graph format glosses over. Fortunately the DSM approach encourages one to put more context into the interaction cells. A DMM (Domain Mapping Matrix) can be used to establish a mapping between two different views of a system, e.g. to relate functions to the component architecture. The tutorial will show you how to model, analyze and improve such a mapping. Cyclic relations can be easily spotted, because the type of relations remain above the diagonal.
One-way ANOVA (cell means model)
We can represent this same directed graph as a matrix, called a designstructure matrix, or DSM, as in the table below. The cells along thediagonal of the matrix are the system components A through H. Each Xin the matrix represents an interaction in the system between twocomponents. You can think of each diagonal cell in the matrix as havinginputs entering from its left and right sides, and outputs exiting fromabove and below. For example, reading across row D, we see thatcomponent D has inputs from elements A, B, and F, represented bythe X marks in row D. Each X mark in the matrix represents aninteraction between two components that may either be an input or anoutput, depending on the perspective you view the matrix from.
How to organize an economic value model for use in pricing design
Each of the components in our matrix may be a microservice, or it may bea code module developed by a team. These“clusters” are groups of elements that are interconnected among themselveswhile being little connected to the rest of the system. An introduction to a powerful and flexible network modeling tool for developing and understanding complex systems, with many examples from a range of industries.
Improving Software Architecture Using a Design Structure Matrix
How do you design such a product to be modular, so that portions of it can be more easily changed or upgraded at different rates? How do you ensure the flow of information among people and teams in a large organization without information overload? These are a few of the problems addressed by a technique called the Design Structure Matrix (DSM), a tool for managing complexity. To date, most of its applications have been in the fields of design and engineering management, but it holds promise for a myriad of applications to many kinds of systems where it is important to find and control patterns of relationships among the system’s elements. It is the equivalent of an adjacency matrix in graph theory, and is used in systems engineering and project management to model the structure of complex systems or processes, in order to perform system analysis, project planning and organization design. Don Steward coined the term "design structure matrix" in the 1960s,[2] using the matrices to solve mathematical systems of equations.
MIT Press
As such, this representation often results in an improved and more realistic execution schedule for the corresponding design activities. In graph theory, a clustering coefficient is a measure of the degree towhich nodes in a graph tend to cluster together. A high clusteringcoefficient is indicative of a small-worldnetwork where theneighbours of any node are likely to also be neighbours of each other. Inour service oriented architecture, a high clustering coefficientrepresents components of subsystems that are highly connected to thatsubsystem, but little connected to other subsystems. As a tool for system analysis, DSM provides a compact and clear representation of a complex system and a capture method for the interactions/interdependencies/ interfaces between system elements (i.e. sub-systems and modules). A design structure matrix consists of a matrix to visualize dependencies of hierarchically organized elements and a set of algorithms which can be applied on the matrix to sort the elements in order to discover layering.
The Design Structure Matrix: A Tool for Managing Complexity
Is there new hope for therapeutic matrix metalloproteinase inhibition? - Nature.com
Is there new hope for therapeutic matrix metalloproteinase inhibition?.
Posted: Fri, 07 Nov 2014 08:00:00 GMT [source]
There is a variety of software tools available, some of which are commercially available, while others have evolved as research tools. To promote and foster the advances these topics, over the years, the DSM Community has formed. It is the goal of the DSM Community to progress the available methods to new problems, to adjust research and tool development to the current and future needs of practice, and to promote the idea of managing the interdependencies in a system. In other words, clusters absorb most, if not all, of the interactions(i.e. DSM marks) internally and the interactions or links betweenseparate clusters are eliminated or at least minimized.
In our example, A makes a directed call to D andE makes a directed call to F. As a management tool, DSM is most commonly applied in project management, and it provides a project representation that allows for feedback and cyclic task dependencies. This is extremely important since most engineering applications exhibit such a cyclic property.
Why software dependencies matter
For example, where the matrix elements represent activities, the matrix details what pieces of information are needed to start a particular activity, and shows where the information generated by that activity leads. In this way, one can quickly recognize which other activities are reliant upon information outputs generated by each activity. Sometimes is it convenient for layout purposes to reverse this, and have the inputs in columns and the outputs in roles. Clustering the items (the metatasks above) is an important part of the DSM method. The goal is generally to cluster items that have a lot of dependencies (or in graph theory terms, sort the items to reduce the lengths of the paths between dependent items).
Welcome to DSMweb.org!
In statistics and in particular in regression analysis, a design matrix, also known as model matrix or regressor matrix and often denoted by X, is a matrix of values of explanatory variables of a set of objects. Each row represents an individual object, with the successive columns corresponding to the variables and their specific values for that object. The design matrix is used in certain statistical models, e.g., the general linear model.[1][2][3] It can contain indicator variables (ones and zeros) that indicate group membership in an ANOVA, or it can contain values of continuous variables. A DSM is represented as a square N x N matrix that maps the elements ofa system with their interactions.
If you have own publications you would like to share, please also do not hesitate to contact us. Services 4 and 5 provide an interesting insight — each of these servicesbelongs to two logical subsystems. These services will naturally havea higher coordination overhead and will likely require the involvement ofan Architect and the support of Delivery Management and EngineeringManagement to execute on effectively. Drawing out these services clusteredby the team assignments highlights the criticality of services 4 and 5 tothe success of the overall system. Reachability refers to the ability to get from one vertex to anotherwithin a graph.
RDF has been described as the data language for the semantic web and connected data. Managing complex systems is therefore a core competency to successfully run any business. This study confirms the results from an earlier US Air Force study, which showed that well-structured software is delivered in half the time, at half the cost, with 8x less bugs. All these aspects except coupling can be easily observed from the source code using an IDE or editor. The impact of the lack of visibility for coupling is that problems with software dependencies often go undetected.
This is a bit too many for learning and experimentation, so we are also looking at something simple that we know well, Roger Martin's Cascading Choices framework, which we have specialized for pricing work. Understanding where these relationships exist in a design is critical, whether the design is for a process, modular system, organization or the ways skills are connected or a market is segmented. An example of a DSM follows, from an MIT course by Professor Olivier de Weck.
A secondaryheuristic is to minimize the distance between feedback loops where theycan’t be avoided. Long feedback loops are problematic because many moresteps of the process will have been started by the time we realize thata failure occurred and we will need to restart. There are severaliterative algorithms for sequencing a DSM available at DSMWeb.
Similarly, reading along a specific row reveals which tasks receive information from the task corresponding to that row (i.e., read along a row to see where a task’s outputs go to become other tasks’ inputs). In many cases, the order of tasks down the matrix corresponds to a timeline. In such a case, marks above the diagonal represent forward information transfer to later (i.e. downstream) tasks. Marks below the diagonal depict information fed back to earlier listed tasks (i.e., a feedback mark) and indicate that an upstream task is dependent on a downstream task.
No comments:
Post a Comment